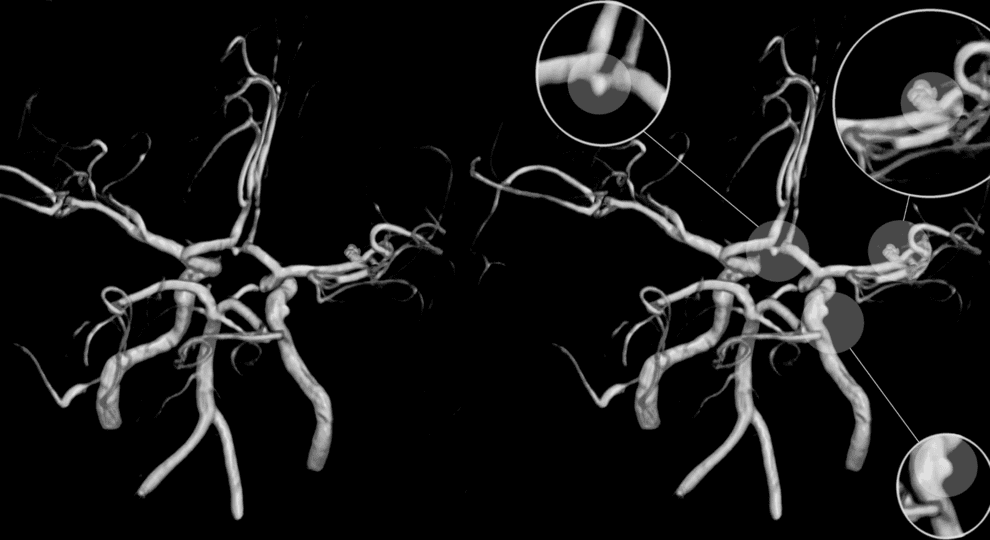
About Aneurysms
Definition
Intracranial aneurysms, also known as cerebral or brain aneurysms, represent a bulging of an artery in the cerebral vascular system. It is defined as a herniation of the intima through a defect in the media of the arterial wall.
While saccular aneurysms are the most common form of intracranial aneurysms, some can present fusiform aneurysms that consist of a global dilation of the arterial wall along its main axis.
Epidemiology
Unruptured intracranial aneurysms (UIAs) are relatively prevalent in the general population, with an estimated global prevalence of 3.2% in adults. The increased utilization of high-resolution imaging has contributed to the growing detection of UIAs.
The risk of rupture for an UIA is approximately 0.25%, translating to 1 in 200 to 400 individuals within the overall population of UIA cases.
Clinical presentation
Unruptured intracranial aneurysm
Unruptured intracranial aneurysms (UIAs) are frequently asymptomatic and are typically discovered either incidentally or during the assessment of neurological symptoms. Less commonly, an intracranial aneurysm may manifest symptoms, including headaches, cranial nerve damage, seizures, or other nonspecific symptoms.
The diagnosis of aneurysms often occurs during evaluations for hemorrhages from another aneurysm.
Ruptured intracranial aneurysm
The primary risk associated with an aneurysm is its potential for rupture. The rupture of an intracranial aneurysm is the leading cause of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Clinically, it manifests as a sudden and intense headache. Additionally, other less specific symptoms may manifest in the event of an aneurysm rupture, including confusion, loss of consciousness, altered general condition, nausea/vomiting, and neurological signs.
Aneurysm rupture carries a significant risk of mortality. Advances in imaging techniques, such as non-invasive three-dimensional imaging, coupled with the development of embolization and improvements in surgery, have contributed to an enhanced survival rate for patients experiencing aneurysmal rupture, decreasing from 50% to 30% over the past few decades. However, the associated morbidity remains substantial, with approximately 40-50% of survivors facing significant functional disability, and 20% enduring severe neurocognitive disorders that hinder their ability to return to work and lead to social and familial isolation.
Risk factors for aneurysm formation
1.Non modifiable risk factors :
Intracranial saccular aneurysms exhibit a higher prevalence in women, with a 3:1 ratio compared to men, even after adjusting for age and comorbidities, particularly in individuals aged ≥30 years. Certain inherited disorders, such as Vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, Marfan syndrome and Fibromuscular dysplasia are associated with a higher occurrence of intracranial saccular aneurysms. Family history and genetics also play a role in aneurysm development.
2. Modifiable risk factors :
Risk factors for aneurysm development
Modifiable risk factors for aneurysms include smoking. The role of hypertension, alcohol use and oral contraceptives as risk factors for aneurysm development is also suggested.
Risk factors for aneurysm growth & rupture
Various factors contribute to the growth and rupture of aneurysms. Identified risk factors for aneurysm growth encompass smoking, younger age, excessive alcohol consumption, aneurysm location and the presence of multiple aneurysms. A history of subarachnoid hemorrhage related to an aneurysm is also considered a risk factor for rupture.
Recent studies indicate that growing aneurysms have an increased likelihood of rupturing, with risk factors for growth involving the initial size of the aneurysm, its relation to arterial branches, hypertension, smoking, and female gender.
Medical imaging & Diagnosis
Unruptured intracranial aneurysm
- Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA) is considered the premier method for diagnosing aneurysms, with 3D rotational angiography enhancing detailed imaging.
- Computed Tomography (CT) with angiography (CTA) is highly sensitive and specific, particularly with modern-generation scanners, making it valuable for aneurysm detection and screening; however, it may have limitations in accurately depicting anatomical details, and artifacts can affect follow-up imaging.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) with angiography (MRA) is effective for detecting aneurysms, offering a non-invasive screening option, and remains useful for follow-up after intervention due to its sensitivity for residual aneurysms, lack of radiation, and reduced invasiveness.
Ruptured intracranial aneurysm
A non-contrast CT scan is the primary diagnostic tool for subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH), demonstrating typical radiological signs and allowing for the identification of complications such as intracerebral hematoma and hydrocephalus.
When CT is inconclusive but SAH is strongly suspected, lumbar puncture is recommended, with cerebrospinal fluid analysis.
Vascular imaging, mainly with CTA, follows a confirmed SAH diagnosis, aiding in aneurysm identification, especially when determined by the SAH pattern and epicenter.
Treatment
Conservative treatment: For patients with unruptured intracranial aneurysms (UIAs) whose risk of treatment complications surpasses the 5-year rupture risk, a conservative approach is recommended. This involves a “wait-and-scan” strategy, incorporating regular imaging to monitor aneurysm growth. Additionally, patients with UIAs should receive guidance on mitigating risk factors for aneurysm growth and rupture, including blood pressure control, smoking cessation, and avoidance of secondhand smoke.
Microsurgical treatment: Microsurgical clipping is the established treatment for intracranial aneurysms, customized based on the aneurysm’s location and type. This procedure, involving an open craniotomy, allows precise control of nearby blood vessels, identification of the aneurysm neck and surrounding branches, and securement of the aneurysm with microsurgical clips. Alternative techniques include wrapping aneurysms when clipping is not feasible, or excluding vessels containing aneurysms through blood flow blockage or Hunterian ligation.
Endovascular treatments: emerging since the 1990s, provide less invasive options for managing intracranial aneurysms by introducing a microcatheter through the femoral or radial artery and guiding it across the brain vasculature. Various strategies exist, with platinum coils to induce thrombosis and occlusion of the aneurysm or other options like intrasaccular devices and intraluminal devices (e.g. flow-diverting stents.)
For ruptured intracranial aneurysms, the initial focus in patient management should prioritize the airway, breathing, and circulation. Emergency stabilization takes place as a priority in the first place.
Complications
Complications associated with the treatment of unruptured aneurysms encompass the general risks associated with any interventional procedure, including infection and hematoma. Additionally, specific complications such as recurrence (indicative of treatment failure), device migration, and thromboembolic events may arise.
Moreover, patients presenting with a rupture can present other complications including:
Re-bleeding: An aneurysm that has previously ruptured or leaked is susceptible to experiencing another episode of bleeding, potentially leading to further harm to brain cells. The risk is higher during the first 72 hours.
Vasospasm may occur after a brain aneurysm rupture. Vasospasm can result in an ischemic stroke, reducing blood flow to brain cells and causing additional cellular damage and loss.
Hydrocephalus, characterized by a buildup of fluid within the brain, is a possible complication. It results in an excess of fluid that puts pressure on the brain and poses a risk of tissue damage.
Prevention
Preventing brain aneurysms cannot usually be done, but certain lifestyle modifications can help mitigate the risk.


